Memories of World War II, known as the bloodiest war in the history of humanity, are still with us, even 73 years later.
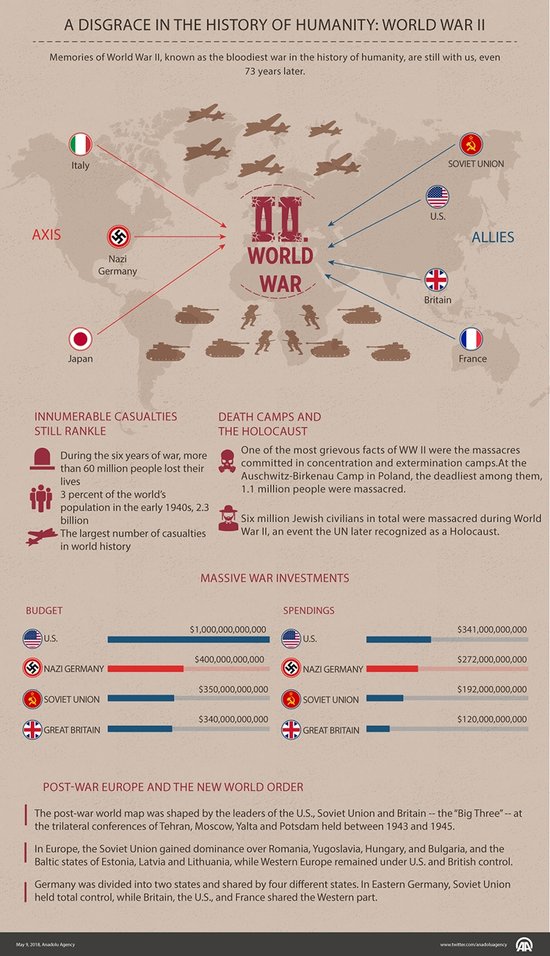
The war between Axis powers led by Nazi Germany (the Third Reich), Italy, and Japan, and the Allies consisting of Britain, France, the U.S. and the Soviet Union, ceased in Europe after Nazi Germany's unconditional surrender on May 9, 1945.
However the Allies waged the war a while longer in the Pacific as Japan refused to surrender. Eventually Japan's unconditional surrender in the wake of the two atomic bombings by the U.S., which cost nearly 150,000 lives, marked the final end of the war on Sept. 2, 1945.
Innumerable casualties still rankle
Despite the 73 years that have since passed, the victims who were able to survive and their descendants still suffer the agony of the devastating war.
World War II, in which 70 million people from both sides were involved, produced the largest number of casualties in world history.
During the six years of war, more than 60 million people -- both combatants and civilians -- lost their lives, or three percent of the world's population in the early 1940s, 2.3 billion.
The death toll climbed to 80 million due to famine and various diseases caused by war.
Millions of civilians in war-battered regions were displaced due to exile, deportation and mandatory evacuation orders by the warring factions.
Especially Nazi Germany's racist policies displaced numerous Jews around Europe, as well as many civilians forced to leave their homes in Finland, Poland, the Baltic states, Serbia and Hungary.
Death camps and the Holocaust
One of the most grievous facts of World War II were the massacres committed in concentration and extermination camps.
At the Auschwitz-Birkenau Camp in Poland, the deadliest among them, 1.1 million people were massacred.
Regarded as one of the greatest tragedies of humanity, the Nazi camps witnessed horrible human experimentation, executions in gas chambers, and crematoriums.
Many Jews and people from other groups became victims of the Nazis' eugenicist policies.
Six million Jewish civilians in total were massacred during World War II, an event the UN later recognized as a Holocaust.
Furthermore, at least 1,800 Japanese-origin Americans died from mistreatment, violence, and malnourishment in internment camps across the U.S. where 127,000 people were placed during the war.
Massive war investments
World War II is also known for huge investments of belligerents in the war industry and the high number of war expenditures.
From a budget of some $1 trillion, from 1940 to 1945, the U.S. spent $341 billion on war.
Nazi Germany, with its $400 billion average budget, spent $272 billion-more than half of its national wealth.
The Soviet Union's war expenditures totaled $192 billion, while it had a $350 billion average budget during the war.
And Britain, with a $340 billion average budget, invested $120 billion on war.
As for arms production, the U.S. army produced 300,000 fighter jets, 89,000 tanks and 363,000 pieces of artillery ammunition.
Soviet arms production consisted of 120,000 jets and 660,000 pieces of artillery ammunition.
Nazi Germany also produced 104,000 jets, 65,000 tanks, and 255,000 pieces of artillery ammunition.
Economic effects of war
During World War II, many of the factories in warring states were used to make ammunition, which resulted in a steep fall in industrial and agricultural productivity.
Thus, European nations' industrial infrastructure was reduced 70 percent in the wake of the war.
Bread was rationed and meat prices boomed in many countries. Food crises were seen in Italy, Austria, and Eastern Europe.
Having lost 27 million population to war, almost no source of funds remained in Soviet Union during the post-war period.
Diseases caused by war
Thousands of war-battered combatants and civilians caught various diseases after the war. Many of them suffered terrible health problems, while many others became disabled or psychologically traumatized.
Numerous American soldiers suffered malaria on the Pacific front, while typhus ruined thousands of people in Europe and North Africa.
Serious health risks emerged after the 1945 U.S. atomic bombings of Japan's Hiroshima and Nagasaki posed a danger for locals decades after the war.
The effects of the bombings caused a variety of diseases, such as deformities, disabilities, and cancer.
Post-war Europe and the new world order
The Allies' victory in World War II succeeded in stopping the menace of Nazism. Nevertheless, the Soviet Union joining the Allies, empowering the communist ideology in Eastern Europe, raised another threat marking the new world order.
The post-war world map was shaped by the leaders of the U.S., Soviet Union and Britain -- the "Big Three" -- at the trilateral conferences of Tehran, Moscow, Yalta and Potsdam held between 1943 and 1945.
In Europe, the Soviet Union gained dominance over Romania, Yugoslavia, Hungary, and Bulgaria, and the Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, while Western Europe remained under U.S. and British control.
Germany was divided into two states and shared by four different states. In Eastern Germany, Soviet Union held total control, while Britain, the U.S., and France shared the Western part.
The Soviet Union's communist expansion in Europe laid the foundation for the bipolar world order.
The post-war political circumstances gave the U.S. a leading role in the Western bloc against the Eastern bloc led by the Soviet Union.
From the 1950s onwards, the Cold War between the U.S. and Soviet Union started and lasted until the early 1990s.